On-premises environments can get an added safety increase from the cloud to detect improper actions on the community.
Microsoft Defender for Identity, previously Azure Advanced Threat Protection, is a cloud-based safety platform that detects compromised identities and uncovers threats and ongoing assaults directed at the on-premises Active Directory. Microsoft Defender for Identity screens person habits and actions and utilizing learning-based analytics. Through the Microsoft Defender for Identity portal, organizations can establish and investigate suspicious user activities and superior assaults.
Understanding the Microsoft Defender for Identity structure
Microsoft Defender for Identity watches community adapters on the area controllers. It captures and parses community visitors, then combines this with Windows occasions instantly from the area controllers. Microsoft Defender for Identity analyzes retrieved occasions and information for assaults and threats. Microsoft Defender for Identity learns about the community by using profiling, deterministic detection, machine studying and behavioral algorithms. The combination of features detects anomalies and warns of suspicious actions.
The core parts of the system are the Defender for Identity portal, Defender for Identity sensor and Defender for Identity cloud service.
What is the Defender for Identity portal?
The portal shows information acquired from the sensors and performs the monitoring, managing and investigating of threats in the community surroundings.
The Defender for Identity Portal has 5 core capabilities:
- creates the Defender for Identity occasion;
- configures the integration with different Microsoft security services;
- manages sensor configuration;
- shows information acquired from the sensors; and
- screens suspicious actions and potential assaults based mostly on the assault kill chain mannequin.
Defender for Identity sensor
The Defender for Identity sensors set up on both the area controllers or servers operating Active Directory Federated Services (ADFS). With the sensor put in on a site controller, there isn’t a want for a devoted server or port mirroring configuration. If put in on an ADFS server, the sensor screens community visitors and authentication occasions instantly.
The Defender for Identity sensor has the following core performance:
- captures and inspects area controller community visitors;
- retrieves Windows occasions from area controllers;
- receives RADIUS accounting info from any VPN suppliers;
- retrieves information about entities similar to customers and computer systems from the Active Directory area;
- performs community decision of entities; and
- transfers information to the Defender for Identity cloud service.
Defender for Identity cloud service
The Defender for Identity cloud service, accessible inside the U.S., Europe and Asia, runs on Azure infrastructure. Defender for Identity cloud service additionally connects on to Microsoft’s Intelligent Security Graph.
Prerequisites for Microsoft Defender for Identity
As with all Microsoft 365 and Azure companies, the first prerequisite is legitimate licensing. To use Defender for Identity, organizations should buy Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) E5 or A5; Microsoft 365 E5, A5 or G5; Microsoft E5, A5 or G5 Security; or the standalone Defender for Identity license.
The area controllers require web entry to the Defender for Identity cloud service; there’s additionally help for proxy servers. The Defender for Identity configuration requires both a normal Active Directory person account or a bunch managed service account. A normal AD person account is the solely possibility for servers that run Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1; each account varieties will work for Windows Server 2012 or greater.
Specific particulars about working programs, ports, protocols and community adapters can be found inside the Microsoft documentation.
Accessing the Defender for Identity portal requires a license and an account designated as a worldwide administrator or safety administrator.
Create the Microsoft Defender for Identity occasion
To use this service, the first activity is to create the Defender for Identity occasion inside the portal at the portal.atp.azure.com URL. You should present credentials utilizing both the customary AD person account or group managed service account, after which you may obtain the required sensor software program.
The Defender for Identity occasion is known as with the Azure Active Directory totally certified area title and created in the information middle situated closest to your Azure Active Directory.
After creating the occasion, click on the supplied hyperlink to obtain the sensor setup. Copy the entry key required to attach the sensor to the occasion. Run the set up on the ADFS server or area controller. The sensor standing, title, model and well being ought to then present in the Microsoft Defender for Identity portal.
The URL for the portal will replace to the title of the occasion. For instance, if the occasion title is coaching, then the new hyperlink is coaching.atp.azure.com slightly than the default URL of portal.atp.azure.com. However, each URLs will work, with the unique URL doing a redirect after logon.
How to work with alerts
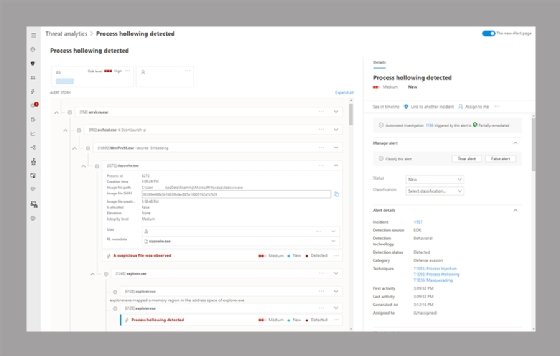
Microsoft Defender for Identity safety alerts makes use of easy language and graphics to indicate suspicious actions in the group’s community. It additionally identifies the actors (customers) and computer systems concerned in the threats. The service colour codes alerts to make it simpler to filter visually and set up by risk part.
A safety alert accommodates the title, description, any proof and an export possibility. The alerts notify safety groups of potential points that may advantage deeper investigation utilizing both the Defender for Identity portal or the Cloud App Security portal.
After an investigation, every alert requires categorization in one in every of three classifications:
- true constructive, that means Defender detects malicious exercise;
- benign true constructive, that means Defender discovered materials proof that was not malicious, similar to exercise from an accepted utility or a penetration take a look at; or
- false constructive, that means a false alarm.
Other alert classes embrace reconnaissance, compromised credentials, lateral motion, area dominance and exfiltration. Each alert sort permits for deeper investigation and evaluate of the carried out motion.
Clicking into the alert shows particulars similar to the system title, username, standing of auto-investigation and verbose alert particulars. The alert additionally shows a hierarchical illustration of all processes associated to the alert.
Additional protections when integrating with Defender for Endpoint
Defender for Identity screens community visitors for account assaults and detects a number of suspicious actions, specializing in areas of reconnaissance, lateral motion cycle and persistence. Defender for Endpoint uncovers refined cyber assaults by evaluating alerts for identified and unknown adversaries.
While Defender for Identity screens the visitors on area controllers, Defender for Endpoint checks the endpoints related to the community. The Microsoft Defender for Identity portal’s configuration part provides the choice to combine the two merchandise for a single interface to verify alerts.
https://searchwindowsserver.techtarget.com/tutorial/Working-with-the-Microsoft-Defender-for-Identity-portal