Overview
The Send E-Mail Smart Service can send emails using a customer sender as long as an email server has been set up.
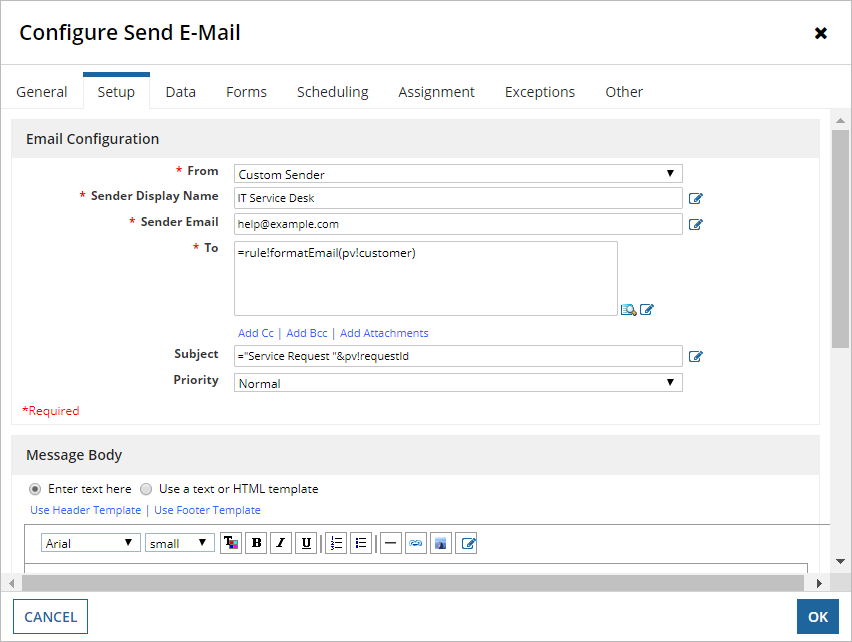
To configure an email with a custom sender:
- Select Custom Sender on the From field of the setup tab. Two new fields will appear below the From field.
- Enter a value for Sender Display Name. This value will be the name of the sender.
-
Enter a value for Sender Email. This value will be the sender’s email.
-
Configure the rest of the Send E-Mail Smart Service as needed. When a process kicks off this activity, the recipient would see an e-mail similar to the one below:
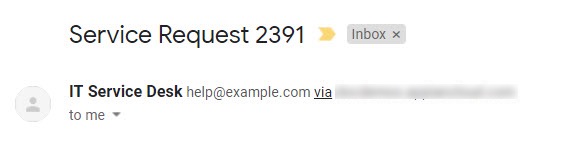
The information that’s displayed to the recipient is dependent on the e-mail client being used.
How custom senders appear to recipients
Custom senders will appear differently to recipients depending on whether Email Sender Authentication is configured for the custom sending domain in the Administration Console.
Without Email Sender Authentication (DKIM) enabled for the sending domain
The detail on Custom Senders below covers the majority of scenarios where Appian sites will have a notification sender address that is different from the custom sender being used. However, there is a very specific scenario where a site shares the same notification address that a process is configured to send from. In this scenario, customers will not see “on-behalf of” or “via” since the sending domain will match between the system and the process. For more information on this, please contact Appian Support.
When Appian’s Custom Sender option is configured to send from an address that is not configured for Email Sender Authentication in the Administration Console, the platform will configure the email headers in a way that makes it clear that the email owner is having a message sent on their behalf, rather than sending the message themselves. This is a best practice that prevents email spoofing and keeps the emails from being flagged as suspicious.
Email spoofing is the sending of emails with a forged sender address. Because Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) does not provide an authentication method, malicious actors can spoof email headers to mislead the recipient about the sender of an email.
Some email providers and clients have built-in email security that detects and notifies users of potential spam and email spoofing. One way this is done is by analyzing email headers. This can be an effective security measure, but it can also lead to legitimate emails being flagged due to improper configuration.
The table below outlines example email header values for this scenario. The platform leverages a custom property called conf.mailhandler.ntf_sndr_addr to set the address that is used for both system-generated notifications and as the default “sender” of an email that originates from the platform.
The configuration above will result in an email that looks something like this:

With Email Sender Authentication (DKIM) enabled for the sending domain
It is often more desirable to send email messages that do not indicate they are being sent “on-behalf of” some other user or system. When Appian’s Custom Sender option is configured to send from an address that is configured for Email Sender Authentication in the Administration Console, the platform will align the required email headers in a way that ensures recipients do not see “on-behalf of” or “via” in their mail client.
While most visible context about an email originating from Appian will be removed, it is not possible to guarantee the behavior of specific clients and there will typically still be information in the email headers (for example, Message-ID that identifies Appian as the system that originated the email.
In the table below, you can find example email header values when Email Sender Authentication is enabled.
Bounced message handling
When a receiving server rejects (“bounces”) a message it will send an email to the “envelope” sender. The “envelope” sender is also known as the MAIL FROM address and is the email address which the sending server uses to actually send the message to the receiving server. It is possible (and common) to have different values for the “envelope” MAIL FROM address and for the FROM address. Note that mail clients will also generally show a Return-Path header which is almost always the same value as the envelope sender address. If it is not, it is generally due to a specific configuration on the receiving server.
Appian Cloud handles bounced messages slightly different – for more information see Email on Appian Cloud.
Custom mail server
In some circumstances it may be necessary for you to make customizations to mail flow that are not configurable on the Appian platform. For more information, see the Mail Server Setup page.
https://docs.appian.com/suite/help/23.2/Configuring_Custom_Email_Senders.html






