Cybersecurity researchers have found a number of safety vulnerabilities in Zimbra e mail collaboration software program that might be probably exploited to compromise e mail accounts by sending a malicious message and even obtain a full takeover of the mail server when hosted on a cloud infrastructure.
The flaws — tracked as CVE-2021-35208 and CVE-2021-35208 — had been found and reported in Zimbra 8.8.15 by researchers from code high quality and safety options supplier SonarSource in May 2021. Mitigations have since been released in Zimbra variations 8.8.15 Patch 23 and 9.0.0 Patch 16.
- CVE-2021-35208 (CVSS rating: 5.4) – Stored XSS Vulnerability in ZmMailMsgView.java
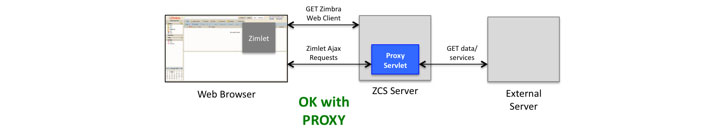
- CVE-2021-35209 (CVSS rating: 6.1) – Proxy Servlet Open Redirect Vulnerability
“A mixture of those vulnerabilities might allow an unauthenticated attacker to compromise an entire Zimbra webmail server of a focused group,” said SonarSource vulnerability researcher, Simon Scannell, who recognized the safety weaknesses. “As a outcome, an attacker would achieve unrestricted entry to all despatched and obtained emails of all workers.”
Zimbra is a cloud-based e mail, calendar, and collaboration suite for enterprises and is obtainable each as an open-source model and a commercially supported model with further options similar to a proprietary connector API to synchronize mail, calendar, and contacts to Microsoft Outlook, amongst others. It’s used by over 200,000 companies throughout 160 international locations.
CVE-2021-35208 issues a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability within the Calendar Invite element that may be triggered in a sufferer’s browser upon viewing a specially-crafted e mail message containing a JavaScript payload that, when executed, grants entry to the goal’s total inbox in addition to the online consumer session, which might then be abused to launch additional assaults.
The drawback stems from the truth that the Zimbra internet shoppers — an Ajax-based desktop consumer, a static HTML consumer, and a mobile-optimized consumer — carry out the sanitization of the HTML content material of incoming emails on the server-side and in a fashion that permits a foul actor to inject rogue JavaScript code.
“The draw back of utilizing server-side sanitization is that every one three shoppers could rework the trusted HTML of an e mail afterwards to show it of their distinctive manner,” Scannell mentioned. “Transformation of already sanitized HTML inputs can result in corruption of the HTML after which to XSS assaults.”
On the opposite hand, CVE-2021-35208 pertains to a server aspect request forgery (SSRF) assault whereby an authenticated member of a company can chain the flaw with the aforementioned XSS situation to redirect the HTTP consumer used by Zimbra to an arbitrary URL and extract delicate info from the cloud, together with Google Cloud API entry tokens and IAM credentials from AWS, resulting in its compromise.
“Zimbra wish to alert its prospects that it’s potential for them to introduce an SSRF safety vulnerability within the Proxy Servlet,” the corporate noted in its advisory. “If this servlet is configured to permit a specific area (by way of zimbraProxyAllowedDomains configuration setting), and that area resolves to an inside IP tackle (similar to 127.0.0.1), an attacker might probably entry companies working on a special port on the identical server, which might usually not be uncovered publicly.”






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HowtoSpecifyaPreferredSMTPServerforaMacOSXMailAccount2016-01-04-568a7f403df78ccc153b7b78.png)
