Mathy Vanhoef
One of the issues that makes Wi-Fi work is its potential to break huge chunks of information into smaller chunks, and vice versa, relying on the wants of the network at a given second. These mundane network plumbing options, it seems, have been harboring vulnerabilities that may be exploited to ship customers to malicious web sites or exploit or tamper with network-connected devices, newly revealed analysis exhibits.
In all, researcher Mathy Vanhoef discovered a dozen vulnerabilities, both within the Wi-Fi specification or in the best way the specification has been carried out in enormous numbers of devices. Vanhoef has dubbed the vulnerabilities FragAttacks, brief for fragmentation and aggregation assaults, as a result of all of them contain body fragmentation or body aggregation. Broadly talking, they permit folks inside radio vary to inject frames of their selection into networks protected by WPA-based encryption.
Bad information
Assessing the impression of the vulnerabilities isn’t easy. FragAttacks permit knowledge to be injected into Wi-Fi site visitors, however they don’t make it doable to exfiltrate something out. That means FragAttacks can’t be used to learn passwords or different delicate info the best way a earlier Wi-Fi assault of Vanhoef, known as Krack, did. But it seems that the vulnerabilities—some which were a part of Wi-Fi since its launch in 1997—might be exploited to inflict different kinds of injury, significantly if paired with different kinds of hacks.
“It’s by no means good to have somebody in a position to drop packets into your network or goal your devices on the network,” Mike Kershaw, a Wi-Fi safety knowledgeable and developer of the open supply Kismet wi-fi sniffer and IDS, wrote in an e mail. “In some regards, these are not any worse than utilizing an unencrypted entry level at a espresso store—somebody can do the identical to you there, trivially—however as a result of they will occur on networks you’d in any other case assume are safe, and might need configured as a trusted network, it is definitely unhealthy information.”
He added: “Overall, I feel they provide somebody who was already focusing on an assault in opposition to a person or firm a foothold they would not have had earlier than, which is certainly impactful, however in all probability don’t pose as enormous a threat as drive-by assaults to the typical particular person.”
While the issues have been disclosed final week in an industry-wide effort that was 9 months within the making, it stays unclear in lots of circumstances which devices have been susceptible to which vulnerabilities and which vulnerabilities, if any, have acquired safety updates. It’s nearly a certainty that many Wi-Fi-enabled devices won’t ever be mounted.
Rogue DNS injection
One of essentially the most extreme vulnerabilities within the FragAttacks suite resides within the Wi-Fi specification itself. Tracked as CVE-2020-24588, the flaw might be exploited in a manner that forces Wi-Fi devices to use a rogue DNS server, which in flip, can ship customers to malicious web sites, fairly than those they meant. From there, hackers can learn and modify any unencrypted site visitors. Rogue DNS servers additionally permit hackers to carry out DNS rebinding attacks, wherein malicious web sites manipulate a browser to assault different devices linked to the identical network.
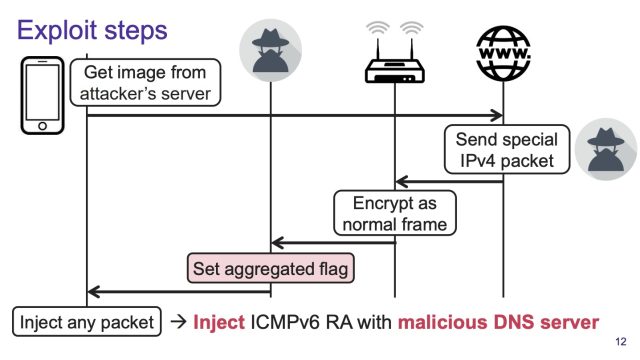
The rogue DNS server will get launched by injecting an ICMPv6 Router Advertisement into Wi-Fi site visitors. Routers sometimes difficulty these bulletins so different devices on the network can find it. The injected commercial instructs all devices to use a DNS specified by the attacker, for lookups of each IPv6 and IPv4 addresses.
An exploit demoed in a video Vanhoef revealed exhibits the attacker luring the goal to an internet site that stashes the router commercial in a picture.
FragAttacks: Demonstration of Flaws in WPA2/3.
Here’s a visible overview:
Mathy Vanhoef
In an e mail, Vanhoef defined: “The IPv6 router commercial is put within the payload (i.e. knowledge portion) of the TCP packet. This knowledge is by default handed on to the appliance that created the TCP connection, within the demo that may be the browser which is anticipating a picture. This implies that by default the shopper will not course of the IPv6 router commercial, however as an alternative processes the TCP payload as software knowledge (right here[‘s] a picture).”
He stated that it’s doable to carry out the assault with out person interplay when the goal’s entry level is susceptible to CVE-2021-26139, one of many 12 vulnerabilities that make up the FragAttacks bundle. The safety flaw stems from a kernel flaw in NetBSD 7.1 that causes Wi-Fi entry factors to ahead Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN frames to different devices even when the sender has not but authenticated to the AP.
It’s protected to skip forward, however for these curious concerning the particular software program bug and the explanation the video demo makes use of a malicious picture, Vanhoef defined:
To make the sufferer course of the TCP payload (i.e. knowledge portion) as a separate packet, the aggregation design flaw in Wi-Fi is abused. That is, the attacker intercepts the malicious TCP packet on the Wi-Fi layer, and units the “is aggregated” flag within the Wi-Fi header. As a end result, the receiver will cut up the Wi-Fi body into two network packets: the primary network packet incorporates a part of the unique TCP header and is discarded. The second packet corresponds with the TCP payload which we made certain will now correspond to the ICMPv6 packet, and because of this the ICMPv6 router commercial is now processed by the sufferer as a separate packet. So proximity to the sufferer is required to set the “is aggregated” Wi-Fi flag in order that the malicious TCP packet will probably be cut up into two by the receiver.
The design flaw is that an adversary can change/set the “is aggregated” flag with out the receiver noticing this. This flag ought to have been authenticated so {that a} receiver can detect if it has been modified.
It’s doable to carry out the assault with out person interplay when the entry level is susceptible to CVE-2020-26139. Out of 4 examined house routers, two of them had this vulnerability. It appears that almost all Linux-based routers are affected by this vulnerability. The analysis paper discusses in additional element how this works—basically as an alternative of together with the ICMPV6 router commercial in a malicious TCP packet it may well then be included in an unencrypted handshake message (which the AP will then ahead to the shopper after which the adversary can once more set the “is aggregated” flag and many others).
Punching a gap within the firewall
Four of the 12 vulnerabilities that comprise FragAttacks are implementation flaws, which means they stem from bugs software program builders launched when writing code primarily based on the Wi-Fi specification. An attacker can exploit them in opposition to entry factors to bypass a key safety profit they supply.
Besides permitting a number of devices to share a single Internet connection, routers stop incoming site visitors from reaching linked devices until the devices have requested it. This firewall works through the use of network deal with translation, or NAT, which maps personal IP addresses the AP assigns every machine on the native network to a single IP deal with that the AP makes use of to ship knowledge over the Internet.
The result’s that routers ahead knowledge to linked devices solely once they have beforehand requested it from an internet site, e mail server, or different machine on the Internet. When a type of machines tries to ship unsolicited knowledge to a tool behind the router, the router robotically discards it. This association isn’t perfect, but it surely does present a significant protection that protects billions of devices.
Vanhoef found out how to exploit the 4 vulnerabilities in a manner that permits an attacker to, as he put it, “punch a gap by means of a router’s firewall.” With the flexibility to join immediately to devices behind a firewall, an Internet attacker can then ship them malicious code or instructions.
In one demo within the video, Vanhoef exploits the vulnerabilities to management an IoT machine, particularly to remotely activate and off a sensible energy socket. Normally NAT would stop a tool exterior the network from interacting with the socket until the socket had first initiated a connection. The implementation exploits take away this barrier.
In a separate demo, Vanhoef exhibits how the vulnerabilities permit a tool on the Internet to provoke a reference to a pc working Windows 7, an working system that stopped receiving safety updates years in the past. The researcher used that potential to acquire full management over the PC by sending it malicious code that exploited a critical vulnerability called BlueKeep.
“That implies that when an entry level is susceptible it turns into simple to assault purchasers!” Vanhoef wrote. “So we’re abusing the Wi-Fi implementation flaws in an entry level as a primary step so as to subsequently assault (outdated) purchasers.”
Getting your repair
Despite Vanhoef spending 9 months coordinating patches with greater than a dozen {hardware} and software program makers, it’s not simple to determine which devices or software program are susceptible to what vulnerabilities and of these susceptible merchandise, which of them have acquired fixes.
This page offers the standing for merchandise from a number of firms. A extra complete listing of identified advisories is here. Other advisories can be found individually from their respective distributors. The vulnerabilities to search for are:
Design flaws:
- CVE-2020-24588: aggregation assault (accepting non-SPP A-MSDU frames).
- CVE-2020-24587: combined key assault (reassembling fragments encrypted below totally different keys).
- CVE-2020-24586: fragment cache assault (not clearing fragments from reminiscence when (re)connecting to a network).
Implementation vulnerabilities permitting the injection of plaintext frames:
- CVE-2020-26145: Accepting plaintext broadcast fragments as full frames (in an encrypted network).
- CVE-2020-26144: Accepting plaintext A-MSDU frames that begin with an RFC1042 header with EtherType EAPOL (in an encrypted network).
- CVE-2020-26140: Accepting plaintext knowledge frames in a protected network.
- CVE-2020-26143: Accepting fragmented plaintext knowledge frames in a protected network.
Other implementation flaws:
- CVE-2020-26139: Forwarding EAPOL frames though the sender shouldn’t be but authenticated (ought to solely have an effect on APs).
- CVE-2020-26146: Reassembling encrypted fragments with non-consecutive packet numbers.
- CVE-2020-26147: Reassembling combined encrypted/plaintext fragments.
- CVE-2020-26142: Processing fragmented frames as full frames.
- CVE-2020-26141: Not verifying the TKIP MIC of fragmented frames.
The only manner to mitigate the menace posed by FragAttacks is to set up all accessible updates that repair the vulnerabilities. People could have to do that on every pc, router, or different Internet-of-things machine that’s susceptible. It’s doubtless an enormous variety of affected devices won’t ever obtain a patch.
The next-best mitigation is to be sure that web sites are all the time utilizing HTTPS connections. That’s as a result of the encryption it offers enormously lessens the harm that may be finished when a malicious DNS server directs a sufferer to a pretend web site.
Sites that use HTTP Strict Transport Security will all the time use this safety, however Vanhoef stated that solely about 20 % of the Web does this. Browser extensions like HTTPS everywhere have been already a good suggestion, and the mitigation they supply in opposition to FragAttacks makes them much more worthwhile.
As famous earlier, FragAttacks aren’t doubtless to be exploited in opposition to the overwhelming majority of Wi-Fi customers, for the reason that exploits require a excessive diploma of talent in addition to proximity—which means inside 100 toes to a half-mile relying on the gear used—to the goal. The vulnerabilities pose a better menace to networks utilized by high-value targets similar to retail chains, embassies or company networks, the place safety is essential, after which almost definitely solely in live performance with different exploits.
When updates develop into accessible, by all means set up them, however until you’re on this latter group keep in mind that drive-by downloads and different extra mundane kinds of assaults will in all probability pose a much bigger menace.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HowtoSpecifyaPreferredSMTPServerforaMacOSXMailAccount2016-01-04-568a7f403df78ccc153b7b78.png)
